ethdos-fold
Follows the ideas of ETHdos (https://ethdos.xyz/blog), but using folding schemes. It uses Sonobe under the hood, compiled to WASM.
Usage
- run native tests:
cargo test --release -- --nocapture - build wasm:
wasm-pack build --target web - serve the web:
python -m http.server 8080
Main idea
This section overviews the ETHdos design adapted to the folding schemes IVC model. Read more about ETHdos original design on the original blog post by it's authors: https://ethdos.xyz/blog, which is built using full-recursion with Groth16 proofs.
We have a directed graph of relations between public keys, where each arrow represents a signature.
For example, the signature of pk_1 over the pk_0, ie. sig_{pk_1}(pk_0), is represented by: pk_0 \longleftarrow pk_1.
Let the following diagram be the relation between the public keys:
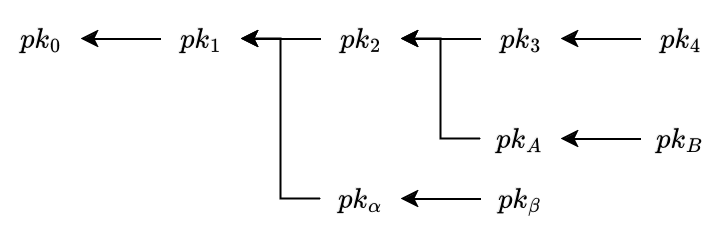
So for example, in the previous diagram:
pk_3is 3 degrees of distance frompk_0pk_3has signedpk_2, who has signedpk_1, who has signedpk_0
pk_Bis 4 degrees of distance frompk_0pk_Bhas signedpk_A, who has signedpk_2, who has signedpk_2, who has signedpk_1
pk_\betais 3 degrees of distance frompk_0pk_\betahas signedpk_\alpha, who has signedpk_1, who has signedpk_0
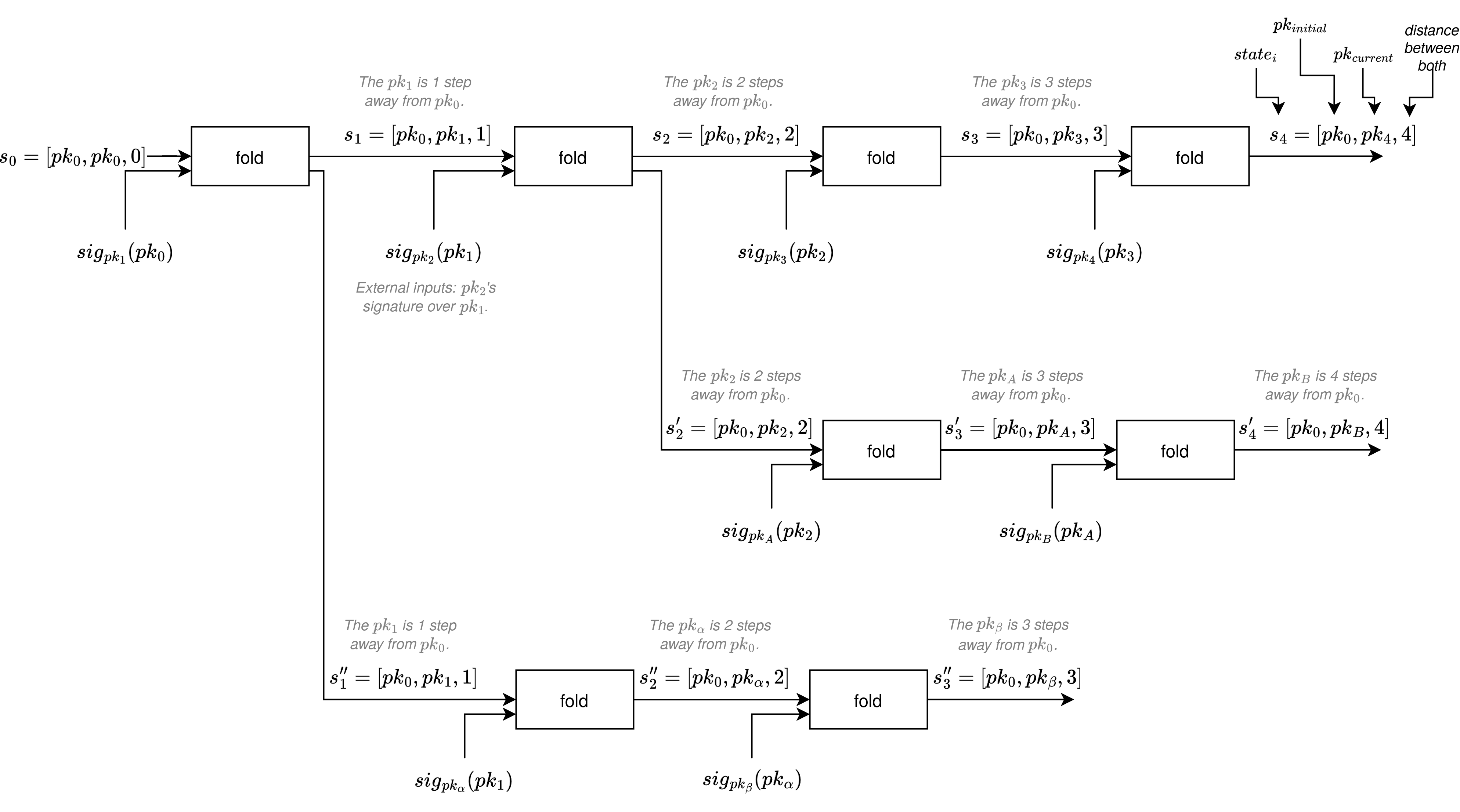
With folding schemes, we can map those relations into an IVC model, where at each recursive step we're proving the FCircuit relation (key part: the method EthDosCircuit.generate_step_constraints).
The state of the IVC is s_i = [pk_0, pk_i, i], where pk_i is the public key i degrees of distance from pk_0. At each step i we have the IVC proof \pi_i, which proves this relation.
Each new folding step, only needs to have the previous step's state (s_i = [pk_0, pk_i, i]) and the respective IVC proof (\pi_i), which proves that the given public key pk_i is i degrees of distance from the public key pk_0.
A new recursive step is done from the \pi_i and the s_i, and by inputing the new signature sig_{pk_{i+1}}(pk_i), which is at degree of distance i+1 from pk_0.
Notice that in order to generate the proof of relations between different public keys, it is not necessary to know any of their private keys, but just by knowing their public keys and having their signatures suffices to generate the proofs.
Some numbers
Current numbers using the Sonobe version at commit
c6f1a246e0705582a75de6becf4ad21f325fa5a1.
Thinkpad laptop, i7-1270P, 16 cores:
- native:
~290msper step - in-browser:
~2.2sper step
Other numbers: due the fixed overhead of folding, current implementation folding 1 single signature per folding step is not ideal. To get more 'real' values, the repo https://github.com/arnaucube/fold-babyjubjubs contains a similar implementation but that performs multiple signature verifications per each folding step, amortizing better the fixed folding costs, reducing the time per signature substantially (eg. on the same laptop it takes ~45ms per signature in the folding step).
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Michael Chu for proposing to build this prototype. This repo uses Sonobe, which relies on arkworks-rs, and for the BabyJubJub EdDSA it uses kilic/arkeddsa. Thanks also to the ETHdos authors, the idea is very cool.